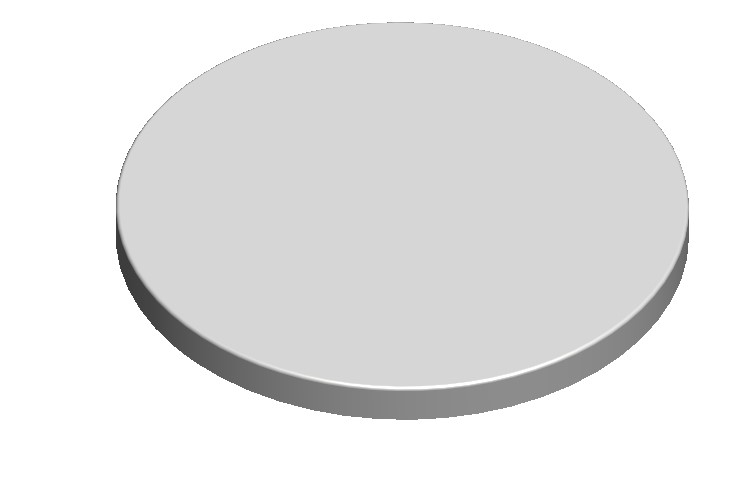
Ideal Vacuum Circular Magnetron Sputtering Targets, TITANIUM - Ti Sputtering Target, 3'' Diameter x 0.25" Thick, 99.995 Percent Purity
Delivery
Payment options
Our advantages
- — 12 months warranty
- — SMS notification
- — Return and exchange
- — Different payment methods
- — Best price
Ideal Vacuum Products, LLC.
This product is a circular magnetron TITANIUM - Ti sputtering target, with a 3'' diameter x 0.25" thickness. It is 99.995% pure.
We use a very competitive pricing strategy to ensure you receive the highest quality products at the best possible value, giving you both affordability and excellence in every purchase. We offer huge discounts to every customer, customers who place bulk orders will enjoy huge savings. We stock huge quantities of our products to give our customers guaranteed same day shipping after placing an order. This short lead time is loved by all our customers who look to manage their cash flow with quicker turnaround times. Our regular customers can maintain lower inventory levels, decreasing storage costs and minimizing the risk of obsolescence. Buying from Ideal Vacuum means a customer receives their product more quickly, enhancing satisfaction and meeting their urgent needs. This also enables our customers to stay ahead of their competition by quickly adapting to new trends and demands.
TITANIUM - Ti
Titanium (Ti) sputtering targets are widely used in thin-film deposition due to titanium’s excellent mechanical, chemical, and physical properties. Here’s a summary of titanium sputtering targets in thin films:
1. Material Properties:
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Titanium is known for its light weight and high mechanical strength, making it ideal for thin films that require durability without adding significant mass.
Corrosion Resistance: Titanium is highly resistant to corrosion, especially in harsh environments such as seawater and acidic conditions.
Biocompatibility: Titanium is biocompatible, which makes it suitable for use in medical devices and biomedical coatings.
2. Deposition Methods:
DC Sputtering: Titanium is a conductive material, so DC magnetron sputtering is commonly used for efficient thin-film deposition.
RF Sputtering: RF sputtering can be used in cases where reactive sputtering or more complex thin-film structures are required.
Reactive Sputtering: Titanium is frequently sputtered in the presence of reactive gases (such as oxygen or nitrogen) to form titanium compounds like titanium dioxide (TiO2) and titanium nitride (TiN).
3. Applications:
Microelectronics: Titanium is used in diffusion barriers, adhesion layers, and electrical contacts in semiconductor devices. It forms thin films that help prevent metal diffusion in integrated circuits.
Optical Coatings: Titanium is used in optical coatings, particularly in anti-reflective coatings, as a durable protective layer. Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is a high-refractive-index material often used in multilayer optical coatings.
Protective Coatings: Titanium thin films are commonly used for corrosion-resistant and wear-resistant coatings in aerospace, automotive, and chemical industries.
Medical Applications: Due to its biocompatibility, titanium is used in thin films for implants, prosthetics, and medical devices to improve their durability and interaction with biological tissues.
Catalysis: Titanium-based thin films (such as TiO2) are used in photocatalysis, particularly in environmental applications like air and water purification.
4. Film Properties:
Mechanical Strength: Titanium films are known for their durability and strength, providing wear resistance and mechanical protection.
Corrosion Resistance: Thin films of titanium are highly resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for use in marine environments and other aggressive chemical conditions.
Adhesion: Titanium thin films often serve as adhesion layers to improve the bonding of other coatings, especially on materials that don’t naturally bond well.
Optical Properties: Titanium dioxide (TiO2) films, formed through reactive sputtering, are highly transparent in the visible range and have a high refractive index (~2.5), making them suitable for optical coatings.
5. Reactive Deposition:
Titanium Dioxide (TiO2): Formed through reactive sputtering in an oxygen environment, TiO2 is used in optical coatings, solar cells, and photocatalysts due to its transparency and high refractive index.
Titanium Nitride (TiN): Formed by sputtering titanium in a nitrogen atmosphere, TiN is used in hard coatings, wear-resistant surfaces, and conductive films in microelectronics.
6. Challenges:
Oxidation: Titanium is reactive, and care must be taken to control the oxidation state, especially during deposition in reactive environments (e.g., forming TiO2 without over-oxidizing the film).
Stress in Films: Titanium thin films can develop internal stress during deposition, which may affect film adhesion and mechanical properties.
Summary:
Titanium (Ti) sputtering targets are widely used in microelectronics, optical coatings, protective layers, and medical devices due to titanium’s high strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. DC sputtering is commonly used for titanium deposition, while reactive sputtering allows the formation of titanium compounds like TiO2 and TiN, which have applications in optics, photocatalysis, and hard coatings. Titanium thin films provide excellent mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and adhesion properties across a broad range of industries.
We use a very competitive pricing strategy to ensure you receive the highest quality products at the best possible value, giving you both affordability and excellence in every purchase. We offer huge discounts to every customer, customers who place bulk orders will enjoy huge savings. We stock huge quantities of our products to give our customers guaranteed same day shipping after placing an order. This short lead time is loved by all our customers who look to manage their cash flow with quicker turnaround times. Our regular customers can maintain lower inventory levels, decreasing storage costs and minimizing the risk of obsolescence. Buying from Ideal Vacuum means a customer receives their product more quickly, enhancing satisfaction and meeting their urgent needs. This also enables our customers to stay ahead of their competition by quickly adapting to new trends and demands.
TITANIUM - Ti
Titanium (Ti) sputtering targets are widely used in thin-film deposition due to titanium’s excellent mechanical, chemical, and physical properties. Here’s a summary of titanium sputtering targets in thin films:
1. Material Properties:
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Titanium is known for its light weight and high mechanical strength, making it ideal for thin films that require durability without adding significant mass.
Corrosion Resistance: Titanium is highly resistant to corrosion, especially in harsh environments such as seawater and acidic conditions.
Biocompatibility: Titanium is biocompatible, which makes it suitable for use in medical devices and biomedical coatings.
2. Deposition Methods:
DC Sputtering: Titanium is a conductive material, so DC magnetron sputtering is commonly used for efficient thin-film deposition.
RF Sputtering: RF sputtering can be used in cases where reactive sputtering or more complex thin-film structures are required.
Reactive Sputtering: Titanium is frequently sputtered in the presence of reactive gases (such as oxygen or nitrogen) to form titanium compounds like titanium dioxide (TiO2) and titanium nitride (TiN).
3. Applications:
Microelectronics: Titanium is used in diffusion barriers, adhesion layers, and electrical contacts in semiconductor devices. It forms thin films that help prevent metal diffusion in integrated circuits.
Optical Coatings: Titanium is used in optical coatings, particularly in anti-reflective coatings, as a durable protective layer. Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is a high-refractive-index material often used in multilayer optical coatings.
Protective Coatings: Titanium thin films are commonly used for corrosion-resistant and wear-resistant coatings in aerospace, automotive, and chemical industries.
Medical Applications: Due to its biocompatibility, titanium is used in thin films for implants, prosthetics, and medical devices to improve their durability and interaction with biological tissues.
Catalysis: Titanium-based thin films (such as TiO2) are used in photocatalysis, particularly in environmental applications like air and water purification.
4. Film Properties:
Mechanical Strength: Titanium films are known for their durability and strength, providing wear resistance and mechanical protection.
Corrosion Resistance: Thin films of titanium are highly resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for use in marine environments and other aggressive chemical conditions.
Adhesion: Titanium thin films often serve as adhesion layers to improve the bonding of other coatings, especially on materials that don’t naturally bond well.
Optical Properties: Titanium dioxide (TiO2) films, formed through reactive sputtering, are highly transparent in the visible range and have a high refractive index (~2.5), making them suitable for optical coatings.
5. Reactive Deposition:
Titanium Dioxide (TiO2): Formed through reactive sputtering in an oxygen environment, TiO2 is used in optical coatings, solar cells, and photocatalysts due to its transparency and high refractive index.
Titanium Nitride (TiN): Formed by sputtering titanium in a nitrogen atmosphere, TiN is used in hard coatings, wear-resistant surfaces, and conductive films in microelectronics.
6. Challenges:
Oxidation: Titanium is reactive, and care must be taken to control the oxidation state, especially during deposition in reactive environments (e.g., forming TiO2 without over-oxidizing the film).
Stress in Films: Titanium thin films can develop internal stress during deposition, which may affect film adhesion and mechanical properties.
Summary:
Titanium (Ti) sputtering targets are widely used in microelectronics, optical coatings, protective layers, and medical devices due to titanium’s high strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. DC sputtering is commonly used for titanium deposition, while reactive sputtering allows the formation of titanium compounds like TiO2 and TiN, which have applications in optics, photocatalysis, and hard coatings. Titanium thin films provide excellent mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and adhesion properties across a broad range of industries.
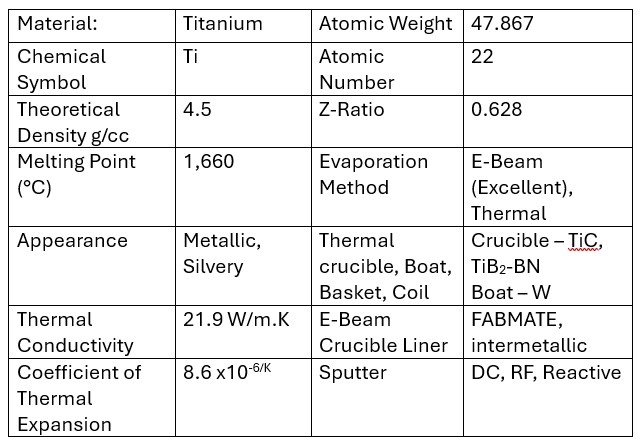
Notes:
Metallic or elastomer backing plate bonding is recommended for all dielectric target materials because these materials have characteristics which are not amenable to sputtering, such as, brittleness and low thermal conductivity. These targets are most susceptible to thermal shock due to their low thermal conductivity and hence, may require specific power ramp up and ramp down procedures during start up and shut down steps.
Please sign in so that we can notify you about a reply











